
23 Aug Dermatitis- Let’s stop the itch!
This time of year, many people – particularly children – have outbreaks as the dry weather irritates dermatitis-prone skin.
What is Dermatitis? Dermatitis is a broad term for skin inflammation. The most common types of dermatitis are atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Let’s look at the differences and what we can do to prevent them.
ECZEMA (ATOPIC DERMATITIS) is one of the most common forms of dermatitis.
‘Atopic’ refers to a tendency to develop allergic conditions such as eczema, asthma, and hay fever.

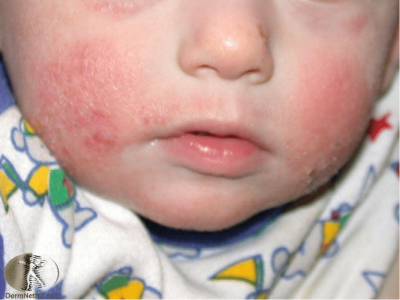
Symptoms: Eczema is a skin condition causing dry, itchy, red skin, which may bleed and crack. The rash can get weepy and crusty, and is prone to infection, as having eczema means that your skin barrier isn’t working properly, making it drier and allowing allergens to enter more easily. It is particularly common in children, usually presenting in infancy and commonly affecting the hands, face, neck, elbows and back of the knees. It is also more prevalent in the drier, winter months.
Causes: Eczema is a chronic genetic condition triggered by environmental factors and in some patients food and airborne allergens.
Prevention/treatment: Eczema in children often will improve with age though there is no cure, we are aiming to manage the condition. Management of the symptoms of eczema include using soap-free cleansers, applying thick moisturiser or emollients regularly and avoiding know triggers. Eczema is also commonly treated with a prescription corticosteroid cream.
CONTACT DERMATITIS is a rash that occurs when the body comes into contact with a substance that either irritates the skin or causes an allergic reaction.
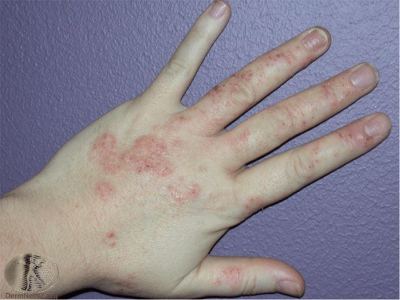

Symptoms: Unlike atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis is a reaction to a particular substance directly on the skin. This rash may burn, sting or itch, and may present with blistering.
Causes: Substances that cause contact dermatitis are divided into ‘irritants’ and ‘allergens.’ Irritant contact dermatitis is caused by the chemical effect of a substance touching your skin, often developing over time through continuous exposure. Water is a common irritant as it weakens the skins barrier function. This type of dermatitis commonly occurs on the hands. Allergic contact dermatitis on the other hand is the result of an allergic reaction in the skin to a certain substance.
Prevention/treatment: Both forms generally fade once exposure to the irritant or allergen subsides, but in the interim treatment includes topical steroid creams and emollients much like the treatment options for eczema.
SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS is another common form of dermatitis.
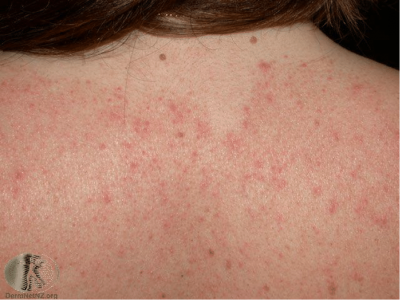

Symptoms: It is a condition which causes greasy yellow scaly patches, red skin and dandruff and affects parts of the body like the face, upper chest and back.
Causes: Seborrheic dermatitis is thought to be triggered by a build-up of yeast that normally lives on the skin, which breaks down oil and inflames the skin. It can be a long-term condition, flaring up with stress, illness, chemical irritants and cold, dry weather. Dandruff is a mild form of this type of dermatitis, and in infants is it known as ‘cradle cap.’ Seborrheic dermatitis can often look like other skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, however unlike eczema it does not always cause itching and it affects oil producing areas of the body rather than hands, elbows and knees as eczema does.
Prevention/treatment: Treatment options include topical antifungal creams, mediated shampoos or a topical corticosteroid cream like other forms of dermatitis.



